Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
Combines two geometries which each other.
The free function union calculates the spatial set theoretic union of two geometries.
template<typename Geometry1, typename Geometry2, typename Collection> void union_(Geometry1 const & geometry1, Geometry2 const & geometry2, Collection & output_collection)
|
Type |
Concept |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Geometry1 const & |
Any type fulfilling a Geometry Concept |
geometry1 |
A model of the specified concept |
|
Geometry2 const & |
Any type fulfilling a Geometry Concept |
geometry2 |
A model of the specified concept |
|
Collection & |
output collection, either a multi-geometry, or a std::vector<Geometry> / std::deque<Geometry> etc |
output_collection |
the output collection |
Either
#include <boost/geometry.hpp>
Or
#include <boost/geometry/algorithms/union.hpp>
The function union implements function Union from the OGC Simple Feature Specification.
![[Note]](../../../../../../../../doc/src/images/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
Boost.Geometry adds an underscore to avoid using the |
|
Case |
Behavior |
|---|---|
|
GeometryOut is a Point |
Calculates union linestrings of input (multi)points |
|
GeometryOut is a Linestring |
Calculates union linestrings of input (multi)linestrings |
|
GeometryOut is a Polygon |
Calculates union polygons of input (multi)polygons and/or boxes |
![[Note]](../../../../../../../../doc/src/images/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
Check the Polygon Concept for the rules that polygon input for this algorithm should fulfill |
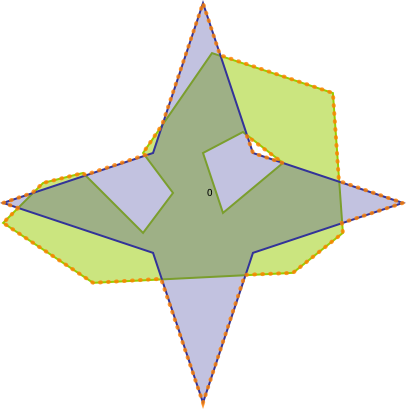
Shows how to get a united geometry of two polygons
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <boost/geometry.hpp> #include <boost/geometry/geometries/point_xy.hpp> #include <boost/geometry/geometries/polygon.hpp> #include <boost/foreach.hpp> int main() { typedef boost::geometry::model::polygon<boost::geometry::model::d2::point_xy<double> > polygon; polygon green, blue; boost::geometry::read_wkt( "POLYGON((2 1.3,2.4 1.7,2.8 1.8,3.4 1.2,3.7 1.6,3.4 2,4.1 3,5.3 2.6,5.4 1.2,4.9 0.8,2.9 0.7,2 1.3)" "(4.0 2.0, 4.2 1.4, 4.8 1.9, 4.4 2.2, 4.0 2.0))", green); boost::geometry::read_wkt( "POLYGON((4.0 -0.5 , 3.5 1.0 , 2.0 1.5 , 3.5 2.0 , 4.0 3.5 , 4.5 2.0 , 6.0 1.5 , 4.5 1.0 , 4.0 -0.5))", blue); std::vector<polygon> output; boost::geometry::union_(green, blue, output); int i = 0; std::cout << "green || blue:" << std::endl; BOOST_FOREACH(polygon const& p, output) { std::cout << i++ << ": " << boost::geometry::area(p) << std::endl; } return 0; }
Output:
green || blue: 0: 5.64795