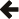#include <boost/range/adaptor/indexed.hpp>
#include <boost/range/algorithm/copy.hpp>
#include <boost/assign.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
template<class Iterator>
void display_element_and_index(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
for (Iterator it = first; it != last; ++it)
{
std::cout << "Element = " << *it << " Index = " << it.index() << std::endl;
}
}
template<class SinglePassRange>
void display_element_and_index(const SinglePassRange& rng)
{
display_element_and_index(boost::begin(rng), boost::end(rng));
}
template<class Iterator1, class Iterator2>
void check_element_and_index(
Iterator1 test_first,
Iterator1 test_last,
Iterator2 reference_first,
Iterator2 reference_last)
{
BOOST_CHECK_EQUAL( std::distance(test_first, test_last),
std::distance(reference_first, reference_last) );
int reference_index = 0;
Iterator1 test_it = test_first;
Iterator2 reference_it = reference_first;
for (; test_it != test_last; ++test_it, ++reference_it, ++reference_index)
{
BOOST_CHECK_EQUAL( *test_it, *reference_it );
BOOST_CHECK_EQUAL( test_it.index(), reference_index );
}
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
using namespace boost::assign;
using namespace boost::adaptors;
std::vector<int> input;
input += 10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90;
display_element_and_index( input | indexed(0) );
return 0;
}
 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries